Ever wondered how a stove fan works? How does warm air move around your room without any external power source? Welcome to the fascinating world of how heat-powered fans work together!
These nifty gadgets work on wood-burning stoves and other hot surfaces, using the heat generated to circulate warm air and make your room cozy.
Unlike traditional fans, they don’t need their own electricity – they create it! And it’s all thanks to a clever device known as a Peltier device.
In this article, we’ll explore how heat-powered stove fans work, the temperature difference they rely on, and why two stove fans might just be better than one!
How Do Heat Powered Fans Work: A Brief Overview
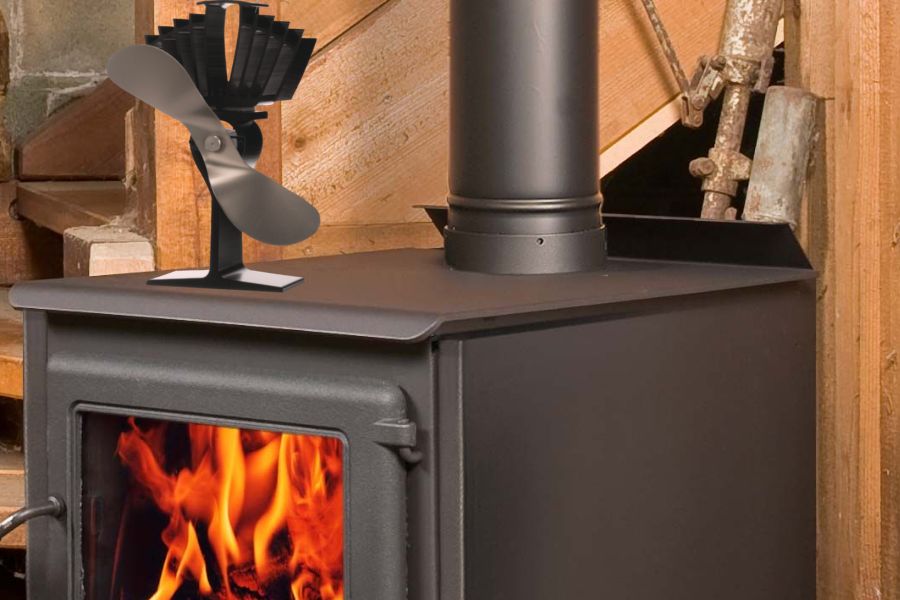

Stove fans, unlike traditional fans, work in a super cool way – by using heat. Here’s how: A wood-burning stove, or any hot flat surface, generates high temperature.
This heat, in turn, triggers the heat-powered stove fan to work. But how does heat make a stove fan whirl? The secret lies in a unique piece of tech called a Peltier device. This device generates electricity when there’s a temperature difference between a hot stove top surface and a cooler area.
This power then spins the fan blades, pushing warm air into the room. Amazing, right? No need for cords or batteries, just good old heat doing its thing. Now, with a stove fan at work, the heat travels, circulating more air, keeping your room snug and comfy.
The Concept Behind Heat-Powered Fans
Understanding heat-powered fans starts with grasping a simple concept: heat-powered fans can generate electricity. Yup, that’s right! The hotter your stove gets, the more juice a heat-powered fan can squeeze out.
The Role of Thermoelectric Generator
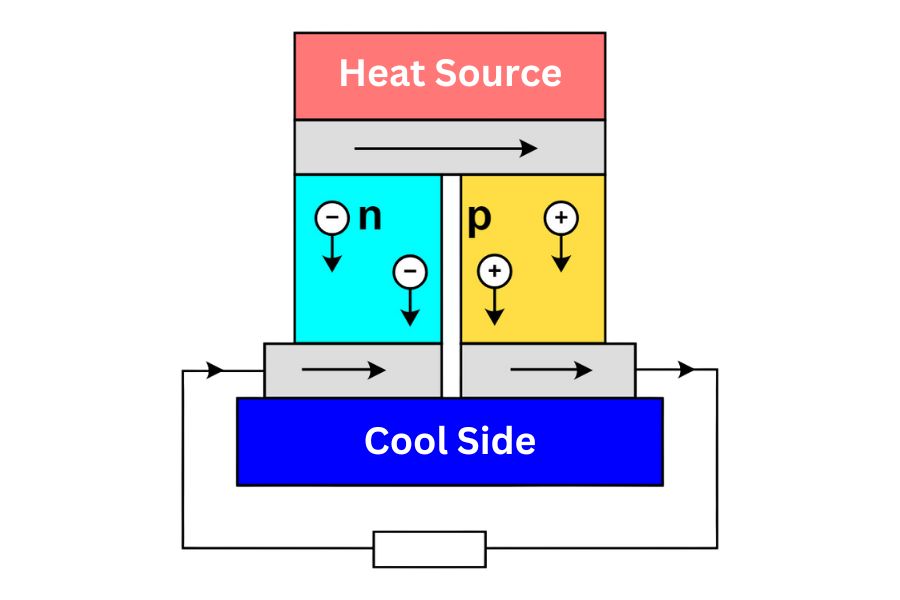
But how does this happen? Here’s where the thermoelectric generator comes into play. This fancy-sounding device is a key part of stove fans.
It’s made up of two dissimilar metals, and when one side gets hot (from the stove), and the other side stays cool, voila! Electricity is generated. This process, known as the Peltier effect, powers the fan blades to move air around your room.
Power Source: Heat and Its Journey
Like a wood-burning stove, the heat source becomes your fan’s fuel. The temperature differential increases as the stove gets hotter, making more electricity.
This powers the fan, pushing out hot air and drawing in cool air from the colder zone of the room. So, the stove fan works to circulate air, making your room a toastier place. The hotter your stove, the harder the fan works. Simple as that!
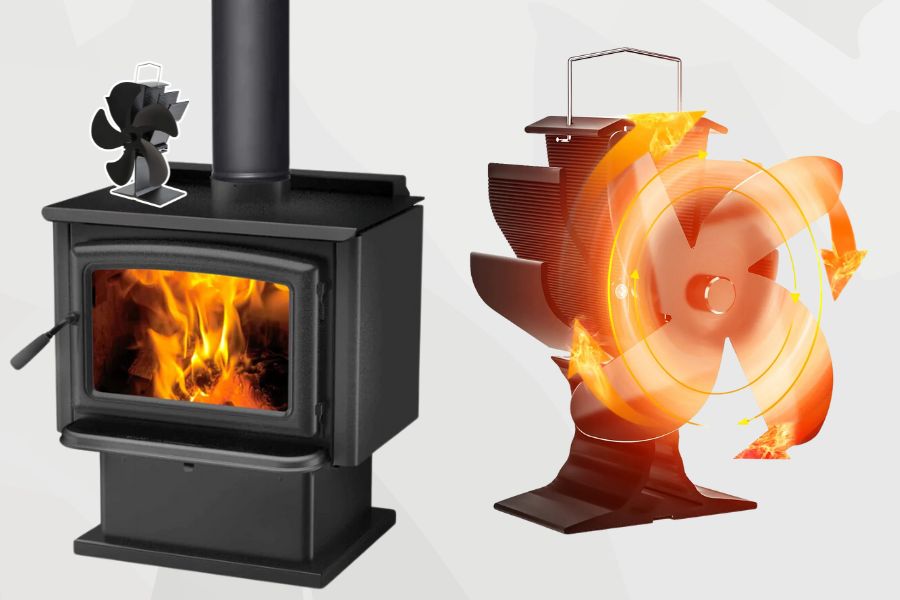
Dissecting a Heat Powered Fan: From Fan Blades to Aluminium Base
A heat-powered fan is a bit like a mini power plant. It’s got fan blades that circulate air, an aluminum base that sits on the stove, and a cool bit of tech called a Peltier device. This device turns heat from the stove into electricity to power the heat-powered fan. Amazing, right?
Hot Surface, Cold Areas: A Temperature Difference Creates a Magic
Here’s where the magic happens. The bottom of the fan sits on the hot surface of a wood-burning stove, while the top is exposed to cooler air.
This difference across the heat-powered fan creates the electricity it needs. The hotter the stove, the more electricity is generated, and the faster the fan blades spin. This clever fan doesn’t need batteries or a plug – it works purely on heat.
So whether you’ve got a traditional wood burner or a modern eco fan, a heat-powered stove fan can make a big difference in your room’s comfort level.
Where Does a Stove Fan Work Best: Wood Burning Stove or Multi Fuel Stove?
If you’re considering getting a heat-powered fan, you might wonder where it works best. Well, the answer is pretty simple: it loves any stove that gets hot! Whether a wood-burning stove or a multi-fuel stove, the fan will work as long as there’s heat.
From Maximum Temperature to Minimum Temperature: The Stove Thermometer’s Reading
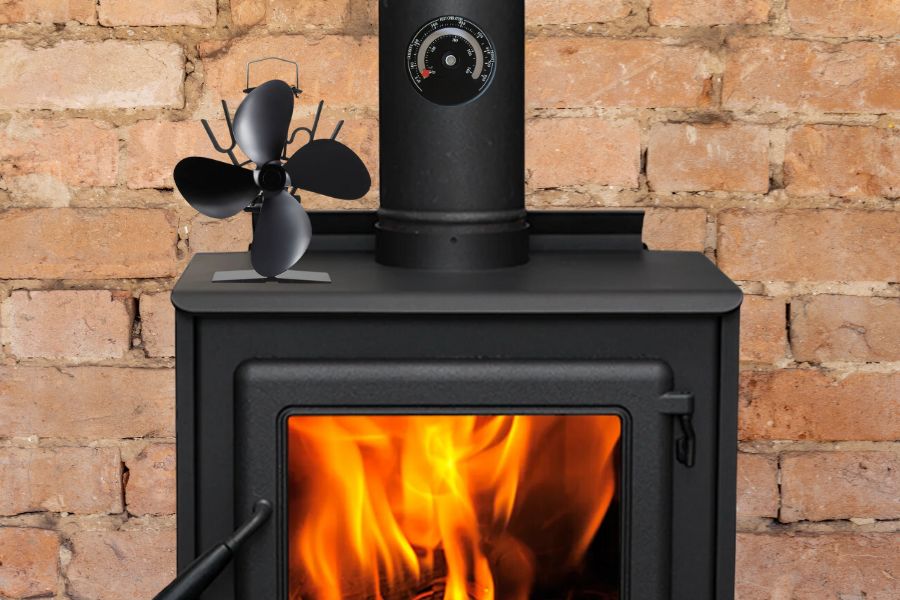

Stove thermometers can tell you how hot your stove is getting. This is key because the hotter your stove, the more electricity the fan can generate.
Just remember: every fan has a maximum and minimum temperature. You must ensure your stove doesn’t get too hot or too cold for your fan.
Wood Stove Fans: Placement and Considerations
Where should you place your wood stove fans? Easy! It goes right on the wood stove’s level surface. But it shouldn’t be too close to the flue pipe as that area might get very hot.
Most models have specifications to help you place the wood stove fan in the right spot. Just ensure there’s enough space for the hot air to circulate, and your room will feel cozy in no time!
Circulating Warm Air: The Art of Heat Distribution
A heat-powered fan is not just a fancy gadget; it’s a master of moving air around. C circulating warm air helps distribute heat evenly throughout your room, making it cozier and more comfortable. No more hot spots near the stove and chilly corners!
Increasing Stove’s Efficiency: More Heat, Less Fuel
One significant advantage of stove fans is that they help your stove work more efficiently. By spreading the heat around, the more stove fan work lets your stove heat up your room quicker.
This means you can use less fuel yet still have a toasty room. More heat, less fuel – that’s what we call efficiency!
From a Log Burner to an Eco Fan: Saving Fuel and Keeping the Room Warm
Whether you have a traditional log burner or a more modern wood stove, a heat-powered stove fan can help you save fuel.
By getting the most out of the heat your stove is producing, you’ll not only keep your room warmer, but you’ll also use less fuel. So, adding a stove fan is a win-win – for your comfort and your wallet!
Delving Deeper: The Thermoelectric Motor, Peltier Device, and Two Dissimilar Metals
Have you ever wondered how a stove fan transforms heat into power without traditional fuel or batteries? It’s all down to a small wonder called a thermoelectric motor.
It uses two dissimilar metals, one exposed to the stove’s high temperature, the other to the cooler surrounding air. This difference creates electricity, like magic!
How Do Heat Powered Stove Fans Work: A Closer Look at the Thermoelectric Phenomenon
The heart of a heat-powered wood stove fan is the Peltier device. It’s the part that takes heat difference and turns it into power. It’s nestled in the heat sink of the fan, keeping the cool side cool.
This is essential as the bigger the heat difference, the more power is generated. So, whether it’s a traditional wood stove fan or one designed for most stoves, they all work on this clever phenomenon. It’s science at work in your living room, helping keep it warm and cozy.
The Value of Heat-Powered Fans: Take Great Pride in Your Stove’s Complete Distribution Capacity
Do you love your stove? You should! It’s a wonderful source of heat. But to fully appreciate its warmth, consider a heat-powered fan. Why? Because it lets your stove show off its complete distribution capacity!
These fans take the very high temperature from your stove, and instead of letting the heat rise to the ceiling, they push it out into the room. They’re like a traditional fan but need no batteries or plugs, just the heat from your stove.
Fuel consumption is a big deal, too. With a fan, your wood stove fans also heat up the room faster and use less fuel.
So, using one wood stove fan or two wood stove fans makes your wood stove much more efficient.
Lastly, always check the model’s specifications. Keep an eye on the maximum temperature on your stove thermometer and avoid areas near the stove pipe where it could get too hot. After all, we want your fan to last and keep your home cozy for many years!






