Gas stoves have been a staple in households for many years, providing a reliable source of heat for cooking and baking. Unlike electric stoves, gas stoves use a flame to heat the burners, transferring heat to the pots and pans. However, one question often arises: why does a gas stove not need to be vented, unlike many other gas-powered appliances?
Ventilation is an important safety measure for gas appliances. This is because it helps to release harmful gases and fumes that could accumulate in a confined space.
Let us explore the science behind gas stoves and examine why they do not need to be vented. We will also examine some safety concerns associated with gas stoves and what steps you can take to ensure their safe operation.
Gas Stove Functionality

Gas stoves work by converting natural gas or propane into heat through a process called combustion. This process involves mixing gas with air and igniting it with a spark or pilot light.
The flame that is produced heats up the burners on the stove, which heat up the pots and pans placed on them. The level of heat can be adjusted by controlling the flow of gas to the burners with the help of knobs or valves.
Types of Gas Stoves
You’ll generally encounter two main types of gas stoves or gas ranges in the market:
Freestanding
Freestanding gas stoves are standalone units that offer the flexibility of placement anywhere in your kitchen layout. These typically come with a control panel situated at the back.
Slide-in
Slide-in gas stoves, on the other hand, are engineered to integrate seamlessly into a designated space within your kitchen countertop. The controls for these are conveniently located at the front.
Both range types offer advantages, depending on your kitchen’s design and personal preferences.
Components of Gas Stoves
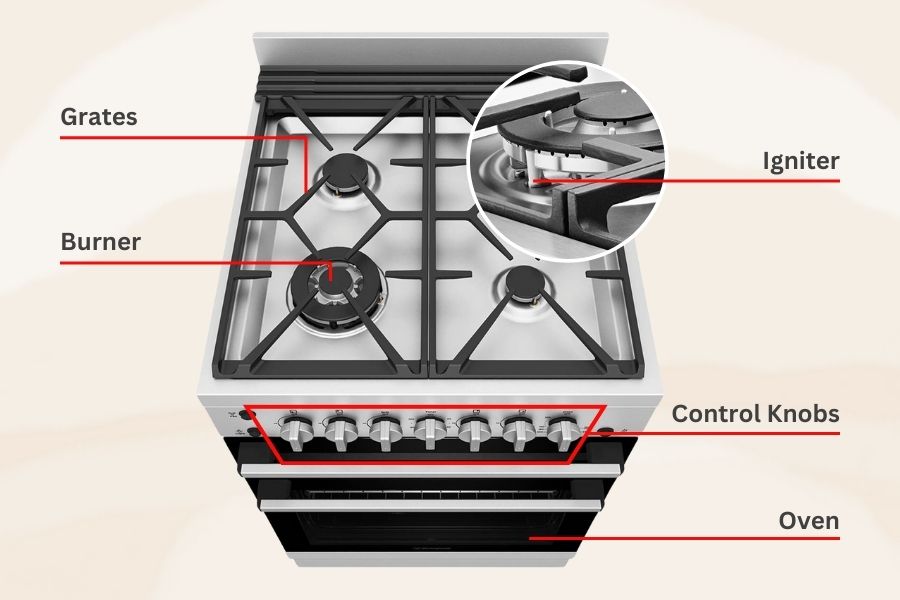
Gas stoves comprise several essential components that synergize to optimize your gas range. These components consist of:
- Burners: These are the stovetop elements where your pots and pans rest. This is also where the all-important combustion process unfolds.
- Grates: These sturdy metal bars are designed to hold up your pots and pans right above the burners.
- Control Knobs or Valves: These handy gadgets are what you use to fine-tune the gas flow to the burners. They let you control the level of heat for your cooking.
- Igniter: This nifty piece of the stove is responsible for generating the spark or pilot light needed to kickstart the combustion process and get cooking with gas.
- Oven: Many gas stoves also feature an oven, which utilizes the same combustion mechanism to heat up the oven’s interior for your baking needs.
Being familiar with how these components interact is vital for making the most of your gas stove’s unique features and ensuring its safe and efficient use.
Venting in Gas Stoves

Venting in residential gas ranges removes the byproducts of combustion from the kitchen through a vent system. The vent system typically includes a hood installed over the stove and a duct that extends to the home’s exterior.
The purpose of venting is to remove the carbon monoxide, smoke, and other harmful gases produced during gas stoves’ combustion.
There are two main venting systems for gas stoves: ducted and ductless. A ducted system uses a duct to exhaust the byproducts of combustion to the home’s exterior. In contrast, a ductless system uses a filter to clean the air and recirculate it back into the kitchen.
Types of Ventilation
Two main types of ventilation are used in gas stoves – external and internal. External ventilation involves venting the combustion byproducts outside the house through a duct system that expels the smoke and gases.
On the other hand, internal ventilation uses a range hood to capture and filter combustion byproducts, releasing them back into the kitchen.
Importance of Ventilation
Ventilation is an important safety feature for gas stoves because the combustion process produces harmful byproducts, including carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, and water vapor. These byproducts can accumulate in the kitchen if not properly ventilated and cause health problems for those in the house.
Carbon monoxide, in particular, is a colorless, odorless gas that can be deadly if not detected and removed from the house.
Alternatives to Venting
While ventilation is important for gas stoves, there are alternatives to traditional venting systems. One such alternative is induction cooktops, which use magnetic fields to heat the cookware, eliminating the need for combustion and venting.
Another alternative is downdraft vents, which are integrated into the cooktop and draw the combustion byproducts down into the vent system rather than up into the air.
It’s important to note that while there are alternatives to venting, proper ventilation is still the safest option for gas stoves. Homeowners should ensure that their gas stoves are properly installed and maintained and that their ventilation systems are functioning correctly to minimize the risks associated with gas stoves.
Reasons for No Venting in Gas Stoves
Though venting is often recommended for gas stoves, there are instances when it might not be necessary. Let’s explore 10 possible reasons for this:
- Efficiency: Some gas stoves are engineered for high efficiency. They produce fewer byproducts of burning gas, thereby reducing the need for external venting.
- Location: Gas stoves positioned in areas with good natural ventilation, like outdoor kitchens, might not require a venting system. Type of Fuel: Propane-burning stoves often emit fewer pollutants, which can eliminate the need for venting in certain scenarios.
- Kitchen Size: In compact kitchens, natural air flow might suffice to prevent the buildup of harmful combustion byproducts.
- Cost: Setting up a venting system can be a financial burden, leading some homeowners to opt out for budgetary reasons. Aesthetic Concerns: Some people may not wish to have a vent hood visible, as it could disrupt their desired kitchen design.
- Noise Level: Ventilation systems can sometimes be loud, which might deter some homeowners from installing one.
- Short Cooking Durations: When you’re just doing quick tasks like boiling water, the volume of combustion byproducts might not warrant a venting system.
- Legal Loopholes: In certain localities, specific types of gas stoves might be exempt from local building codes related to ventilation. Infrequent
- Usage: For those who seldom use their gas stoves, the amount of combustion byproducts generated might not necessitate a venting system.
While it’s true that some gas stoves may not need to be vented, it’s crucial for homeowners to still employ safety measures. For instance, installing carbon monoxide detectors and closely monitoring the stove during use can go a long way in ensuring a safer cooking environment.
Safety Concerns

While gas stoves are convenient and efficient, they also pose several safety concerns. Here are some of the most common safety concerns associated with gas stoves:
Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
Carbon monoxide is a colorless, odorless gas produced during the combustion process of gas stoves. If not properly ventilated, carbon monoxide can accumulate in the kitchen and cause serious health problems, including carbon monoxide poisoning.
Symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning can include headaches, dizziness, nausea, and even death in severe cases. Homeowners should install carbon monoxide detectors in their homes. They must also ensure that their gas stoves are properly ventilated to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning.
Fire Hazards
Gas stoves present a risk of fire if not used properly. The flame from the stove can ignite nearby materials, such as curtains or towels if they are too close to the stove. Oil or grease spills on the stove or surrounding areas can also ignite and cause a fire.
Homeowners should use caution when cooking with gas stoves. They must ensure that flammable materials are kept away from the stove and clean up any spills immediately.
Gas Leaks
Gas leaks are a serious safety concern associated with gas stoves. They can occur if the gas lines or connections are damaged or not properly installed. Gas leaks can be dangerous as gas is highly flammable and can cause an explosion or fire.
Homeowners should be aware of the signs of a gas leak. They include the smell of gas, hissing sounds near the gas lines or connections, or dead vegetation near the gas lines. If a gas leak is suspected, homeowners should evacuate the area immediately and contact a professional to inspect and repair the gas lines.
Burns
Gas stoves can also pose a risk of burns if not used properly. The flames and hot surfaces of the stove can cause burns if touched or if a pot or pan is accidentally tipped over.
Homeowners should use caution when cooking with gas stoves, ensuring that they wear appropriate clothing and use oven mitts or potholders when handling hot pots or pans.
Electric Shock
Electric shock is a potential safety concern if the gas stove is not properly grounded. Electrical current can flow through the metal components of the stove, causing an electric shock if touched. Homeowners should ensure that their gas stove is properly grounded and use grounded outlets when plugging.
Gas stoves pose several safety concerns that homeowners should be aware of. It is important to take proper precautions, such as proper ventilation, installing carbon monoxide detectors, and ensuring the stove is installed and maintained properly to safely use gas stoves.
Gas Stove Functionality and Safety Guides:
- What is an auto-ignition gas stove?
- What is an infrared gas stove?
- Does a gas stove need electricity?
- Do gas stoves have pilot lights?
- Do gas stoves turn off automatically?
Conclusion: Gas Range Venting
Gas stoves are common in many homes, offering many benefits such as convenience, efficiency, and ease of use. However, it is important to understand the science behind their functionality and safety concerns.
While gas stoves do not need to be vented, they can still pose safety concerns, such as carbon monoxide poisoning, fire hazards, gas leaks, burns, and electric shock. Homeowners should take proper precautions and be aware of the safety concerns associated with gas stoves to ensure the safe and efficient use of the appliance.
By understanding the science and safety concerns associated with gas stoves, homeowners can make informed decisions about their use and maintenance, ultimately leading to a safer and more enjoyable cooking experience.






